Rootstock - Alchemy RPC Provider
A step-to-step guide for developers to interact with Rootstock network with the Alchemy RPC Provider.
It aims to address the challenges faced by developers when trying to access critical information like logs, transactions, and balances through RPC, which can significantly impact the timely development of dApps on the Rootstock blockchain.
In this guide you will learn:
- How to create an Alchemy project to make your first API call.
- View some options to interact with the node RPC with the Alchemy sdk and tools.
Prerequisites
Before you start this guide, make sure you have the following:
- Basic understanding of smart contracts and how to interact with them on the Rootstock blockchain.
- Familiarity with Ethereum-based dApp development can be helpful.
- Ensure you have a development environment set up for interacting with blockchain nodes.
- Basic programming knowledge of JavaScript, Python, or other supported languages to make
API calls. And familiarity with making HTTP requests and handling JSON responses.
Who Is It For?
- Developers looking to interact with the Rootstock nodes.
Features
Easy Setup
- Create an API key effortlessly to initiate development.
- Make your first API call in minutes.
API Key Authentication
- Provides secure authentication for decentralized applications (dApps).
- Limits API requests on a daily or monthly basis.
Getting Started
To access the Alchemy tools, visit its Dashboard Portal. If you don't already have an account, you can sign up for free. And then, simply log in to get started.
Step 1: Create New App
After logging in, you'll be directed to the main dashboard. From there, you have different options for interacting with Alchemy tools.
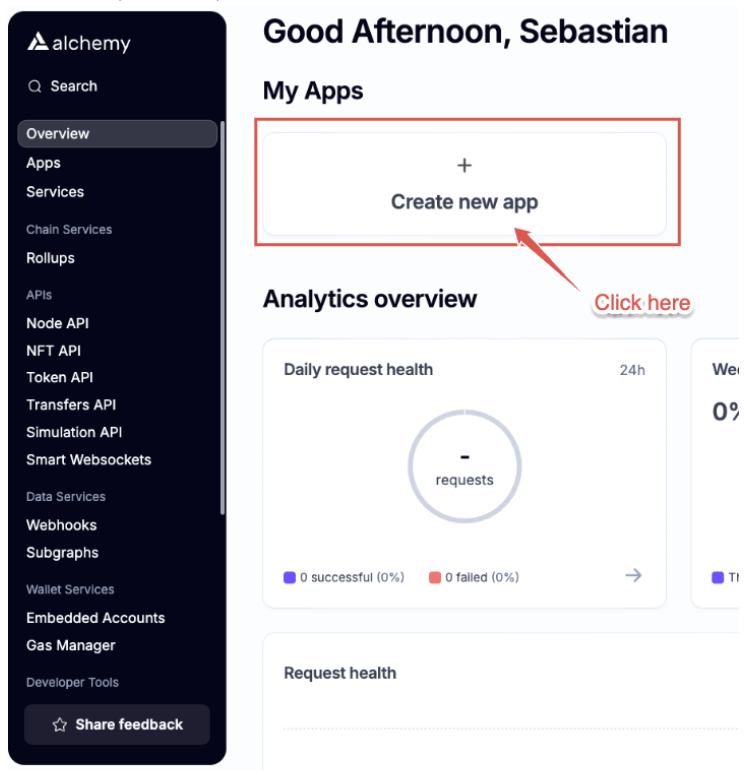
Click the option Create new app, where you'll be prompted to provide the app's name, description, and specify its intended use case.
- Name: This is your app's unique identifier. Choose a meaningful and descriptive name to help you easily recognize the app in your dashboard. This name will appear throughout the platform and may be used in API references.
- Description (Optional): Provide additional information about the app's purpose or functionality. While this field is optional, it's a good practice to include a brief description to help you or your team members understand the app's role or features, especially when managing multiple apps.
- Use Case: Specify how you plan to use the app. Alchemy provides options such as Defi, Analytics, Gaming, Wallet, among others. Choosing the correct use case helps configure the app properly for its intended environment, ensuring it performs optimally for development, testing, or live deployment.
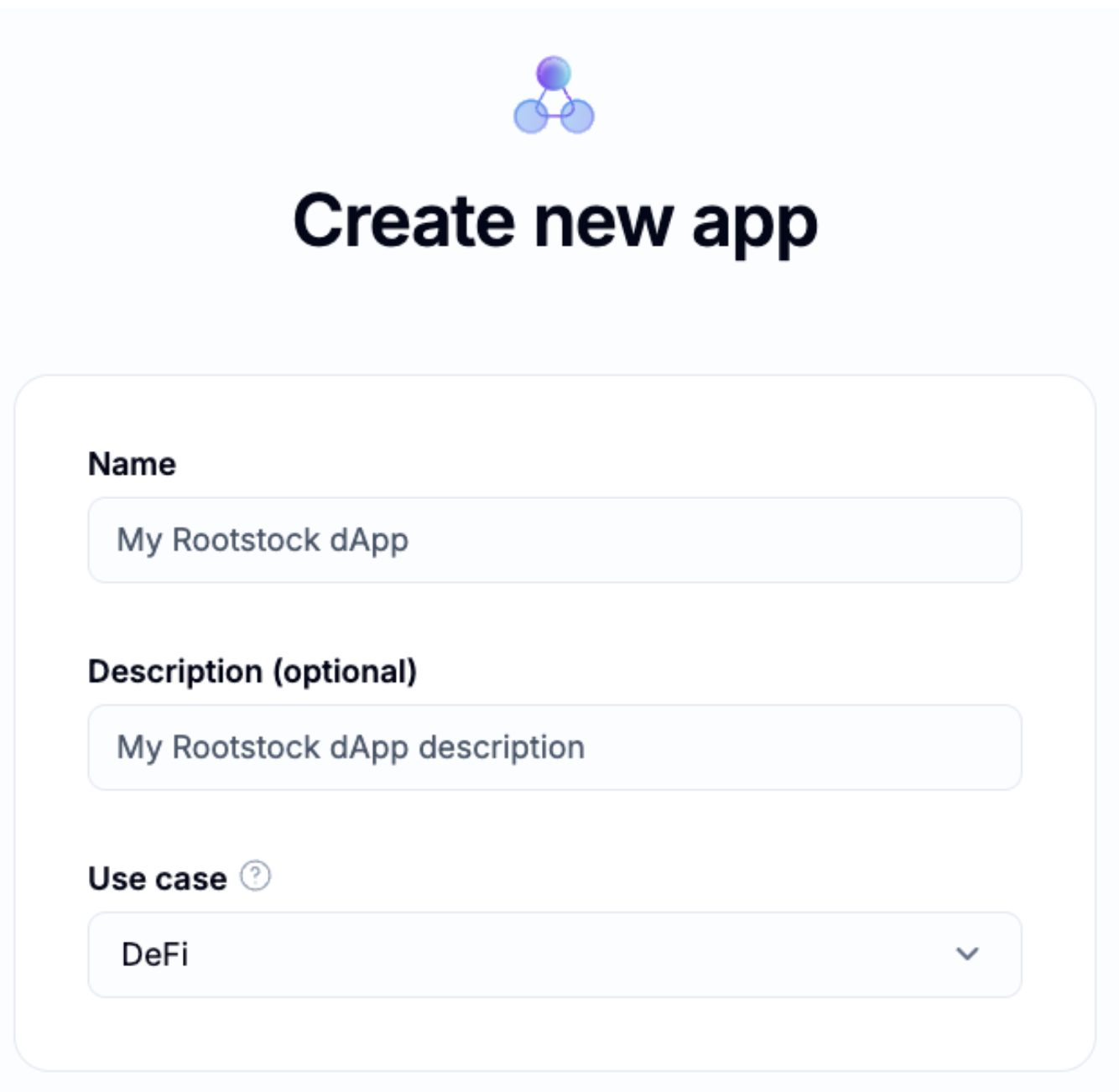
Step 2: Choose Chains
After clicking Next, you'll be prompted to select the network for your dApp. In the Search field, type Rootstock, then click on the Rootstock node. Once selected, click the Next button to proceed.
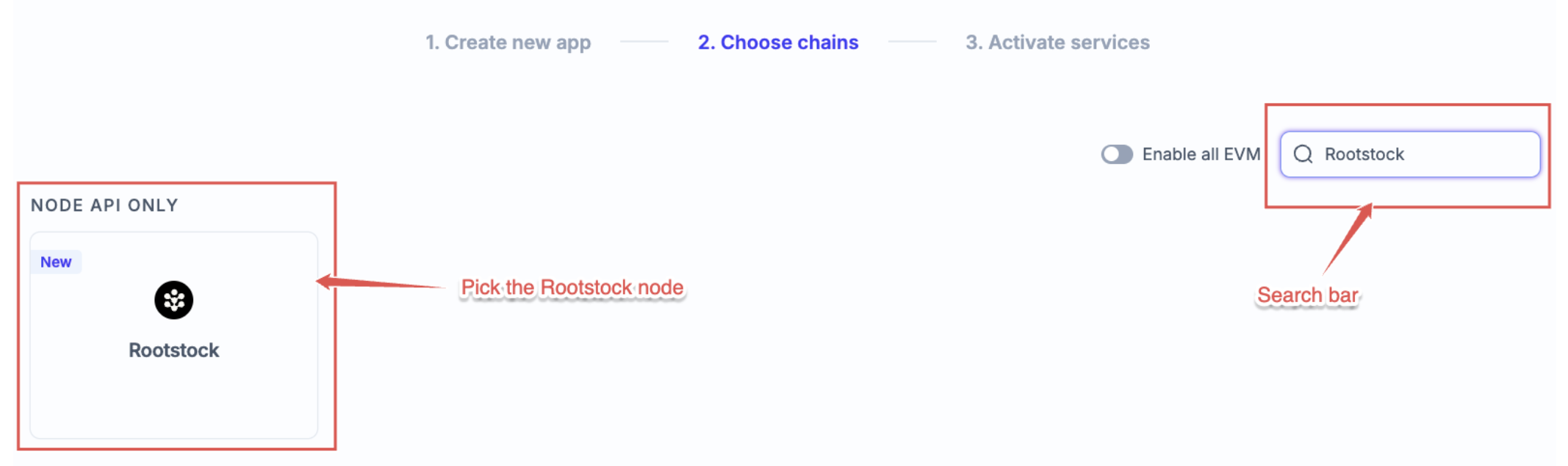
Step 3: Activate Services
The next screen will display the services available for the Rootstock network, including NODE API. Click on Create app to complete the setup.
Your app information will now be visible, similar to the example shown.
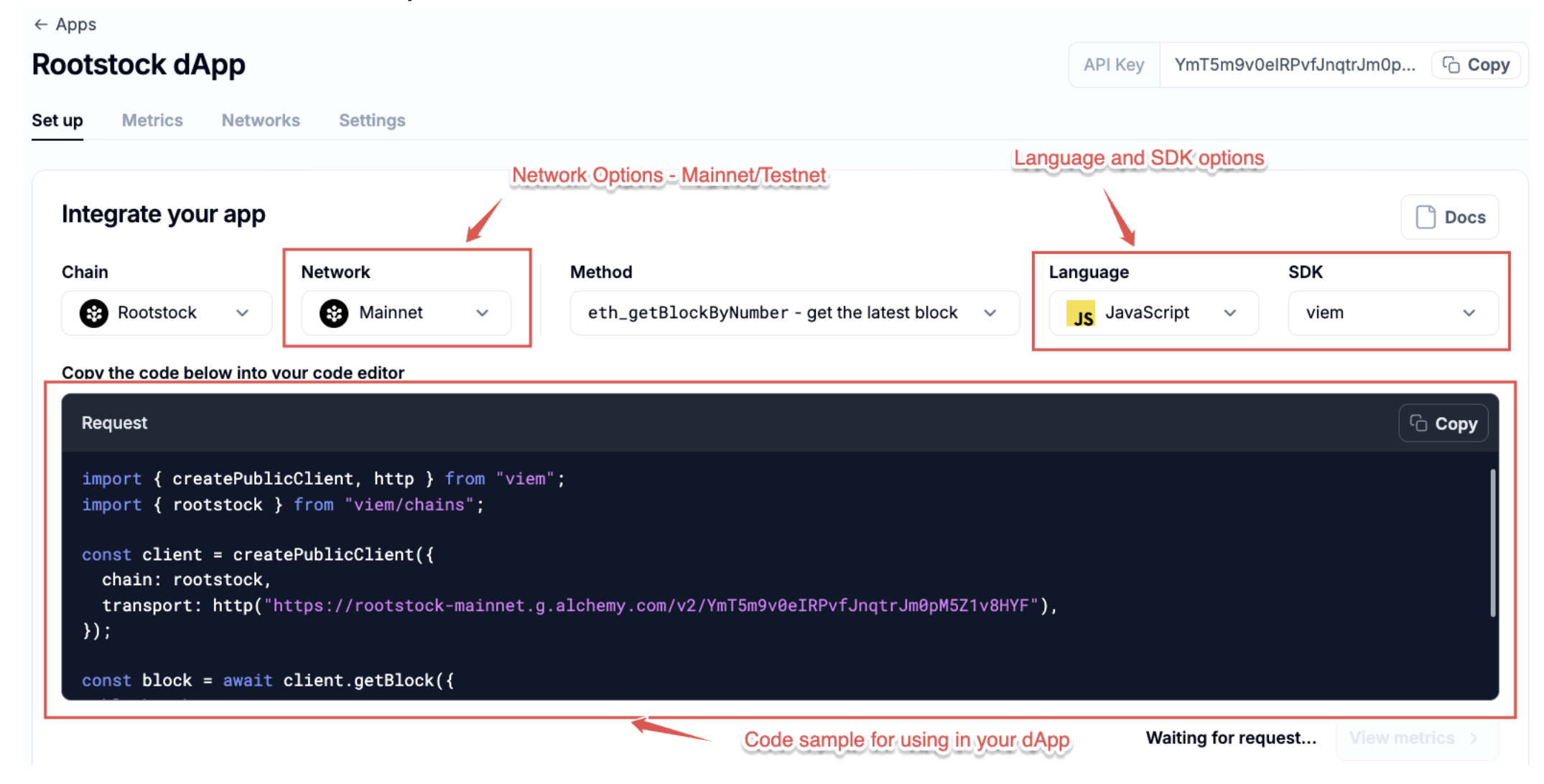
Set Up Tab
In the Setup tab you will see different options for using the rpc node, depending on the Method, Language and SDK you need to use for it.
By default, the dashboard shows an example for the get latest block call on Javascript and Viem.
import { createPublicClient, http } from "viem";
import { rootstock } from "viem/chains";
const client = createPublicClient({
chain: rootstock,
transport: http("https://rootstock-mainnet.g.alchemy.com/v2/<API_KEY>"),
});
const block = await client.getBlock({
blockNumber: 123456n,
});
console.log(block);
However, you will have different language options available for the rpc call, included CLI (command line interface).
Language Options
- CLI (Command Line Interface): No SDK options are available with this choice.
- JavaScript: You can choose from Viem, Ethers.js, or Fetch as your SDK options.
- TypeScript: Only the Viem SDK option is available for selection.
- Python: You can select web3.py as the SDK option.
Is it possible to test the CLI option easily in your console by pasting the following code:
curl -X POST https://rootstock-mainnet.g.alchemy.com/v2/<API_KEY>\
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-d '{
"jsonrpc": "2.0",
"method": "eth_getBlockByNumber",
"params": ["latest", false],
"id": 1
}'
And the response should look like this:
{"jsonrpc":"2.0","id":1,"result":{"number":"0x67a9c4","hash":"0xe3d0d2b47eb0a06f04cea614355a6ba10935c62596e188e3d27dcafb7ddc746f","parentHash":"0x140a94c77bc08077133d874405252b4463bcbfe500cc7a9e48f4626cdfd91104","sha3Uncles":"0x1dcc4de8dec75d7aab85b567b6ccd41ad312451b948a7413f0a142fd40d49347","logsBloom":"0x00000000000000000000101000000000000080000040000000000000000000000020400000010000000000000000001000002000000000000008800000000000000000000000000000000000000008000000000000000001000000000000000000000000000000000040000000000000000000000000000000000000020000000001000000000081000000000004000000000000000000000000000020000000000000000200100020000000000000000180000000000080001000020000000000000001000000000000000000008000000030000000000000200000100000000000000000000000002004000880000000000400000000000000200010000200" …
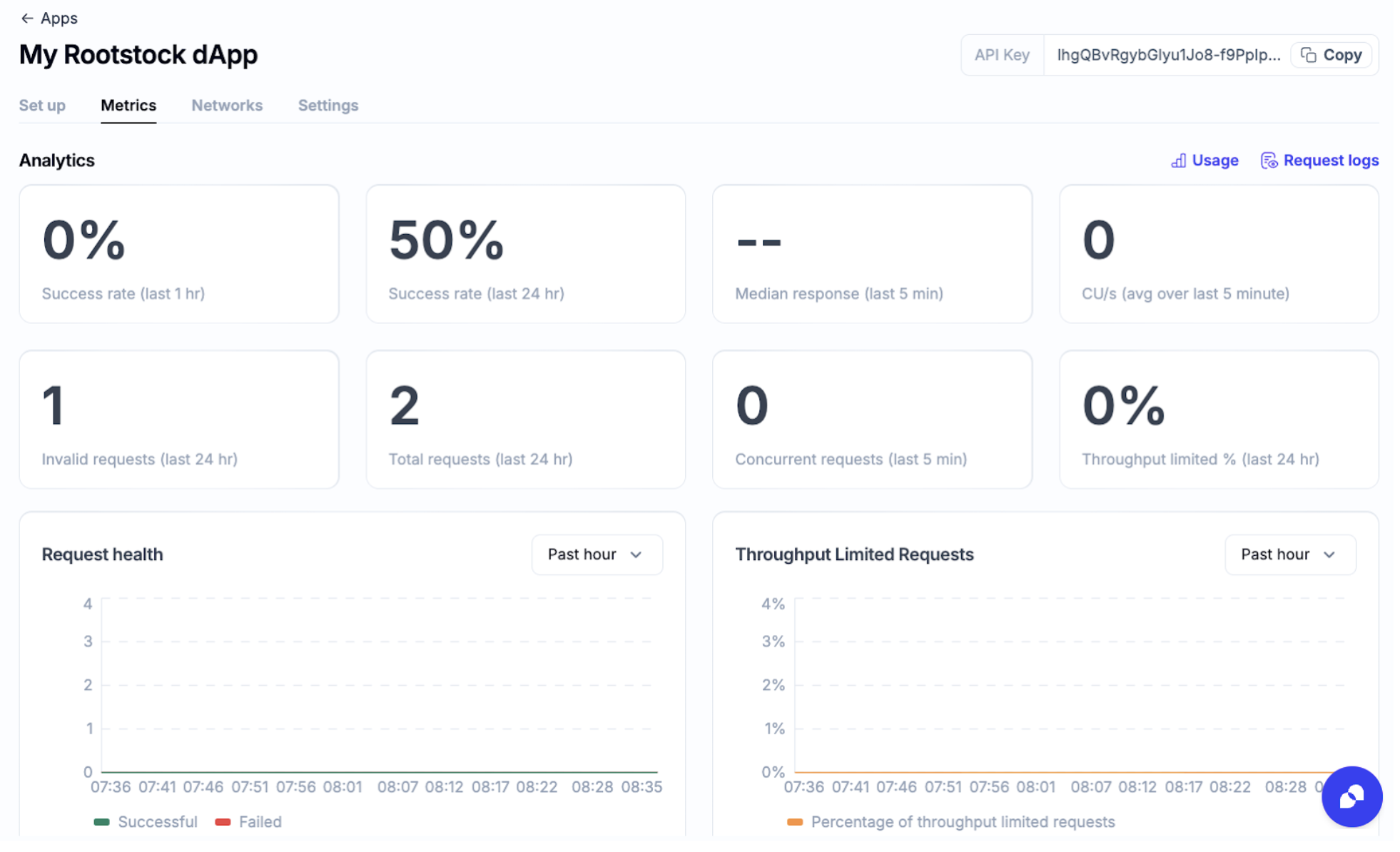
Metrics Tab
In this tab, you can see the analytics for your app, with the success rates and total requests.
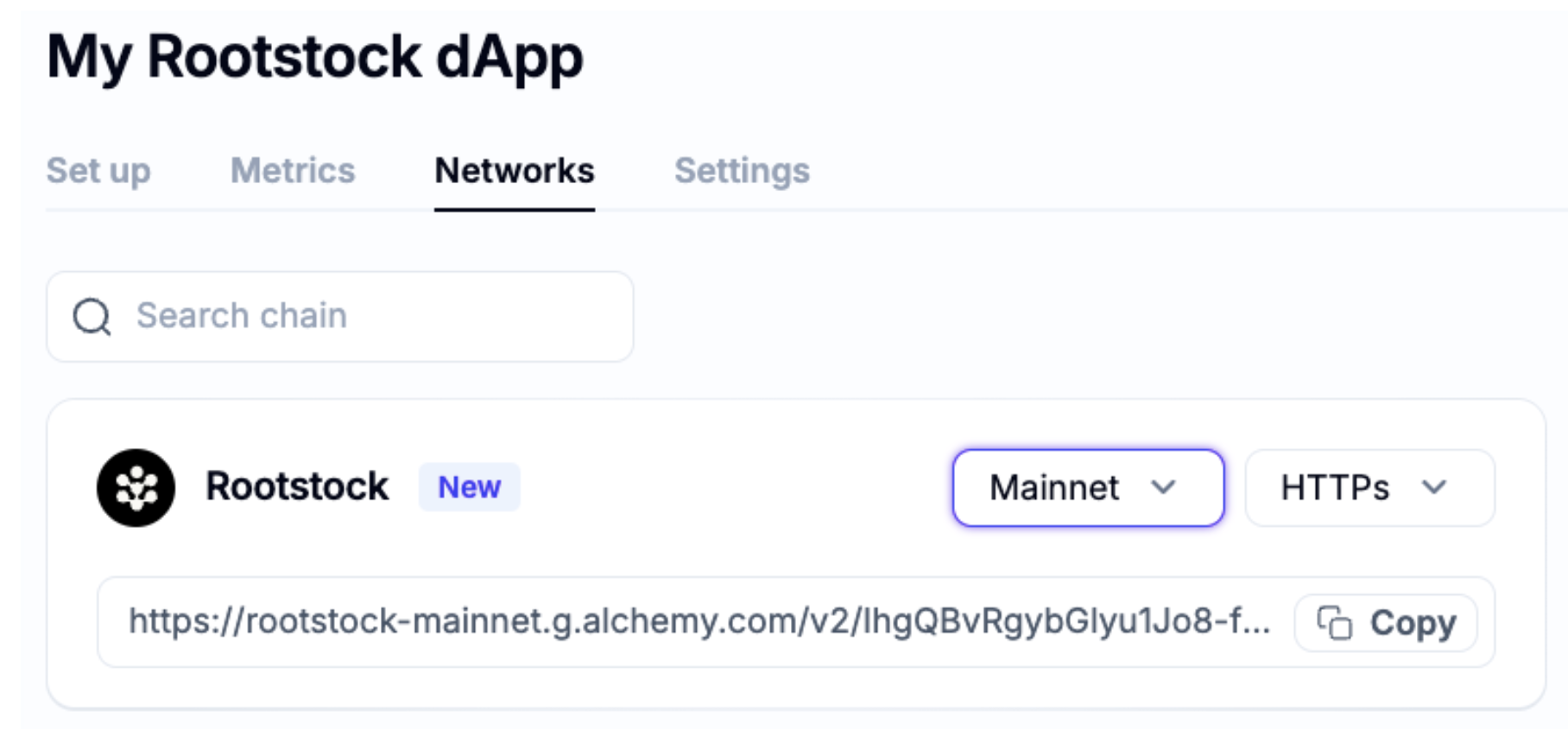
Networks Tab
In this tab, you will find the Rootstock card, where you can copy the RPC url you will use in your dApp (mainnet or testnet).
Settings Tab
In this tab you find different configuration options of your app, like advanced config, allow list, JWT keys, or delete your app from the Alchemy dashboard.
Conclusion
The use of RPC API is an important part of the frontend and backend interaction with the blockchain. Alchemy is a poweful platform which contains a lot of tools that can be used for developers to create their code faster.